Service hotline 0755-83261303
Email:ht@htsemi.com
Address315 Huachang Road, Dalang Street, Longhua District, Shenzhen
Semiconductor "Black Technology": What is Gallium Nitride (GaN)?
 发表时间:2023-11-03
发表时间:2023-11-03 浏览量: 192
浏览量: 192
Gallium nitride (GaN) is known as the third generation semiconductor material after the first generation of Ge and Si semiconductor materials, the second generation of GaAs and InP compound semiconductor materials. Today, let's take a brief look at what this material has to offer.
R&D background
Gallium nitride (GaN) is an artificial material synthesized in 1928. The conditions for the natural formation of gallium nitride (GaN) are extremely harsh, requiring high temperatures of over 2000 degrees Celsius and nearly 10000 atmospheres of pressure to synthesize gallium nitride (GaN) from metal gallium and nitrogen, which is impossible to achieve in nature. After 70 years of technological improvement, it was widely used in light-emitting diodes in the 1990s. Initially, it was used to manufacture light-emitting diodes with colors ranging from red to ultraviolet.
Understanding Gallium Nitride (GaN)
Gallium nitride (GaN) is an inorganic substance, with the chemical formula GaN. It is a compound of nitrogen and gallium and is a direct bandgap semiconductor. This compound has a structure similar to wurtzite and high hardness. GaN is an extremely stable compound and a hard high melting point material, with a melting point of approximately 1700 ℃.
In terms of physical appearance, gallium nitride (GaN) is generally a yellow powder, similar to lead zinc ore crystals, with a molar mass of 83.73 g/mol g · mol ⁻ ¹, The melting point is above 2500 ° C and the density is 6.15 g/cm3. It can react with water and is not flammable.
Later, it was discovered in the application process that gallium nitride (GaN) crystals can grow on various substrates, including sapphire, silicon carbide (SiC), and silicon (Si). Growing GaN epitaxial layers on silicon can utilize existing silicon manufacturing infrastructure, eliminating the need for costly specific production facilities, and can use low-cost, large-diameter silicon wafers.
Application scope
Gallium nitride has a wide range of applications and is currently widely used in military electronics, communication, optoelectronics, and other fields. Moreover, gallium nitride (GaN), as a wide bandgap compound semiconductor material, has advantages such as large bandgap width, high breakdown voltage, high thermal conductivity, high switching frequency, and strong radiation resistance.
Among them, high switching frequency means that the application circuit can use smaller passive components; A high breakdown voltage means that the voltage tolerance is higher than that of traditional silicon materials, and it does not affect the conduction resistance performance, thus reducing the conduction loss. With various advantages, gallium nitride has become a key material to better support the lightweight of electronic products, and is currently the most promising material for development.
Gallium nitride (GaN) has significantly better performance than first and second generation semiconductor materials such as silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), gallium arsenide (GaAs) in high-power, high-temperature, high-frequency, radiation resistant microelectronics, and short wavelength optoelectronics. They possess superior performance such as high frequency, efficiency, high power, high pressure resistance, high temperature resistance, and strong radiation resistance, which are in line with major national strategic needs such as energy conservation and emission reduction, intelligent manufacturing, and information security. They are key core materials and electronic components that support the independent innovation, development, transformation, and upgrading of industries such as next-generation mobile communication, new energy vehicles, high-speed rail trains, and energy internet, It has become the focus of global semiconductor technology and industry competition.
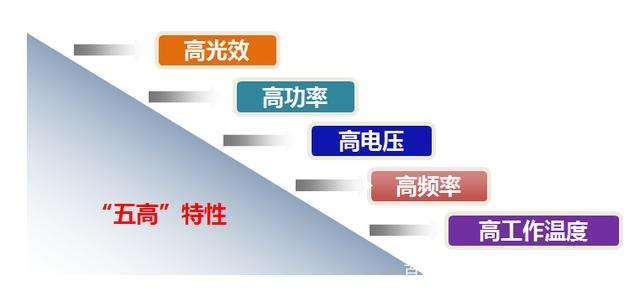
Every invention and application of new materials is an impact on the industry, with both challenges and opportunities in the impact. Mastering the application of new materials has great development significance for manufacturers, industries, and even countries. The development and current situation of gallium nitride vividly illustrate this point - now, the track belonging to gallium nitride has opened, and there is still a long way to go, let's wait and see!
Recruitment
0755-83240725
Cooperation
QQ:3001784606
3001784606

Tel
0755-83261303
Message